A review of the risks that the Federal Reserve needs to pay attention to in the early stages of interest rate cuts
马里奥看Web32024/08/27 02:16
By:马里奥看Web3
Summary On August 23, 2024, Federal Reserve Chairperson Powell officially announced at the Jackson Hole Global Central Bank Annual Meeting that "now is the time for policy adjustments. The direction forward is clear, and the timing and pace of interest rate cuts will depend on upcoming data, changing prospects, and the balance of risks." This also means that the nearly three-year Fed tightening cycle has ushered in a turning point. If there are no surprises in the macro data, the first interest rate cut will occur at the interest rate meeting on September 19. However, when entering the early stage of the interest rate cut cycle, it does not mean that the surge is coming soon. There are still some risks worth being vigilant about. Therefore, the author summarizes some of the most important issues that need attention at present, hoping to help everyone avoid some risks. In general, in the early stage of the interest rate cut, we still need to pay attention to six core issues, including the recession risk of the US, the pace of interest rate cuts, the QT (quantitative tightening) plan of the Federal Reserve, the risk of inflation reignition, the efficiency of global central bank linkage, and the political risk of the US.
First, a rate cut does not necessarily mean an immediate rise in the risk market, but rather a decline in most cases
The adjustment of the Federal Reserve's Monetary Policy has a profound impact on the global Financial Marekt. Especially in the early stage of interest rate cuts, although interest rate cuts are usually seen as measures to stimulate economic growth, they are also accompanied by a series of latent risks, which means that interest rate cuts do not necessarily mean an immediate rise in the risk market, but rather a decline in most cases. The reasons for this situation can usually be classified as follows:
1. Increased Financial Marekt Volatility
Interest rate cuts are usually seen as a signal of support for the economy and the market, but in the early stages of interest rate cuts, the market may experience increased uncertainty and volatility. Investors often have different interpretations of the Fed's actions, and some may believe that interest rate cuts reflect concerns about economic slowdown. This uncertainty can lead to significant fluctuations in the stock and bond markets. For example, during the financial crises of 2001 and 2007-2008, although the Fed began a rate cut cycle, the stock market still experienced significant declines. This was because investors were concerned that the severity of the economic slowdown exceeded the positive impact of interest rate cuts.
2. Inflation risk
Interest rate cuts mean lower borrowing costs, encouraging consumption and investment. However, if interest rate cuts are excessive or prolonged, they may lead to increased inflationary pressures. When abundant liquidity in the economy chases limited goods and services, price levels may rise rapidly, especially when supply chains are restricted or the economy is close to full employment. Historically, such as in the late 1970s, the Fed's interest rate cuts have led to the risk of soaring inflation, which has forced subsequent more aggressive interest rate hikes to control inflation and trigger economic recessions.
3. Capital outflows and currency depreciation
The Fed's interest rate cuts usually reduce the US dollar's interest rate advantage, causing capital to flow from the US market to higher-yielding assets in other countries. This capital outflow will put pressure on the US dollar exchange rate, leading to a depreciation of the US dollar. Although a depreciation of the US dollar can stimulate exports to some extent, it may also bring the risk of imported inflation, especially in the case of high raw material and energy prices. In addition, capital outflows may also lead to financial instability in Emerging Markets countries, especially those that rely on US dollar financing.
4. Instability of the financial system
Interest rate cuts are usually used to alleviate economic pressure and support the financial system, but they may also encourage excessive risk-taking. When borrowing costs are low, Financial Institutions and investors may seek higher-risk investments to obtain higher returns, leading to the formation of asset price bubbles. For example, after the bursting of the technology stock bubble in 2001, the Federal Reserve cut interest rates significantly to support economic recovery, but this policy to some extent fueled the subsequent bubble in the real estate market, ultimately leading to the outbreak of the 2008 financial crisis.
5. Limited effectiveness of policy tools
In the early stages of interest rate cuts, if the economy is already close to zero interest rates or in a low interest rate environment, the Fed's policy tools may be limited. Over-reliance on interest rate cuts may not effectively stimulate economic growth, especially when interest rates are close to zero, which requires more unconventional Monetary Policy measures such as Quantitative Easing (QE). In 2008 and 2020, the Fed had to use other policy tools to deal with economic downturns after interest rate cuts were close to zero, indicating that the effect of interest rate cuts is limited in extreme cases.
Let's look at historical data. Since the end of the Cold War between the US and the Soviet Union in the 1990s and the entry of the world into a global political pattern dominated by the US until now, the Monetary Policy of the Federal Reserve has reflected a certain degree of lag. Currently, it is also in the stage of intense confrontation between China and the US, and the breakdown of the old order undoubtedly exacerbates the uncertainty and risk of policy.
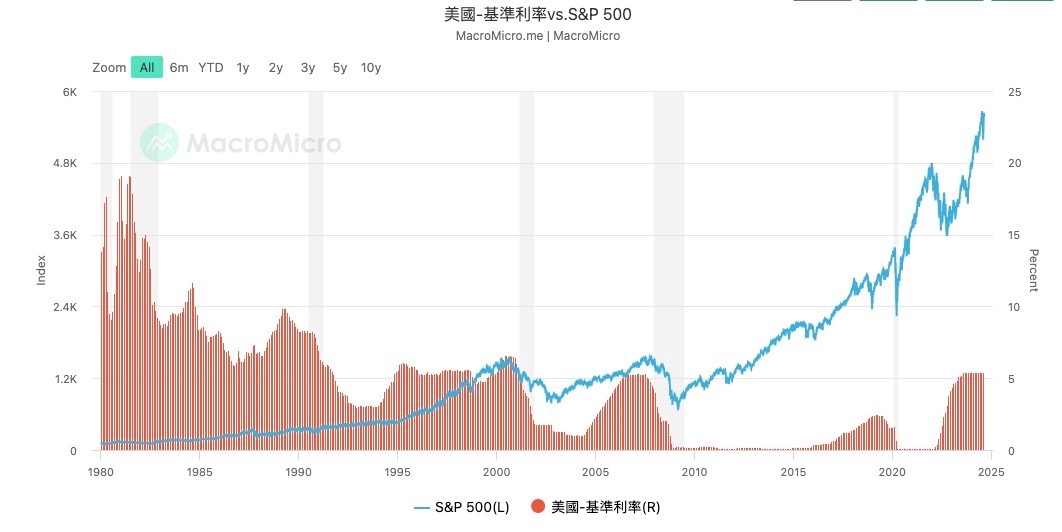
Second, take stock of the main risk points in the current market
Next, let's take stock of the main risk points in the current market, focusing on the recession risk of the US, the pace of interest rate cuts, the QT (quantitative tightening) plan of the Federal Reserve, the risk of inflation reignition, and the efficiency of global central bank linkage.
Risk 1: US Recession Risk
Many people refer to the potential interest rate cut in September as a "defensive interest rate cut" by the Federal Reserve. The so-called defensive interest rate cut refers to the interest rate cut decision made to reduce the potential risk of economic recession in the absence of significant deterioration in economic data.
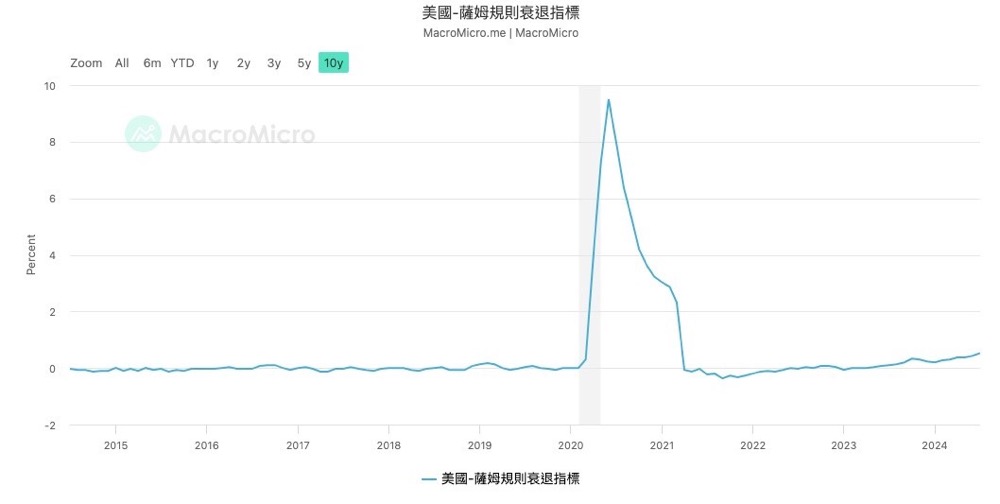
In my previous article, I have analyzed that the US unemployment rate has officially set off the "Sam's Rule" warning line for recession Therefore, it is extremely important to observe whether the interest rate cut in September can curb the gradually rising unemployment rate and thus stabilize the economy and resist recession.
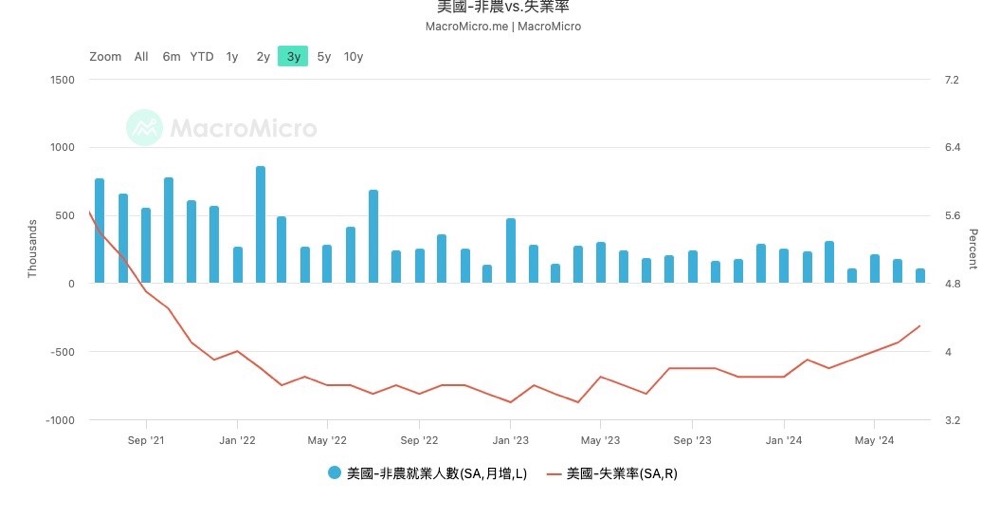
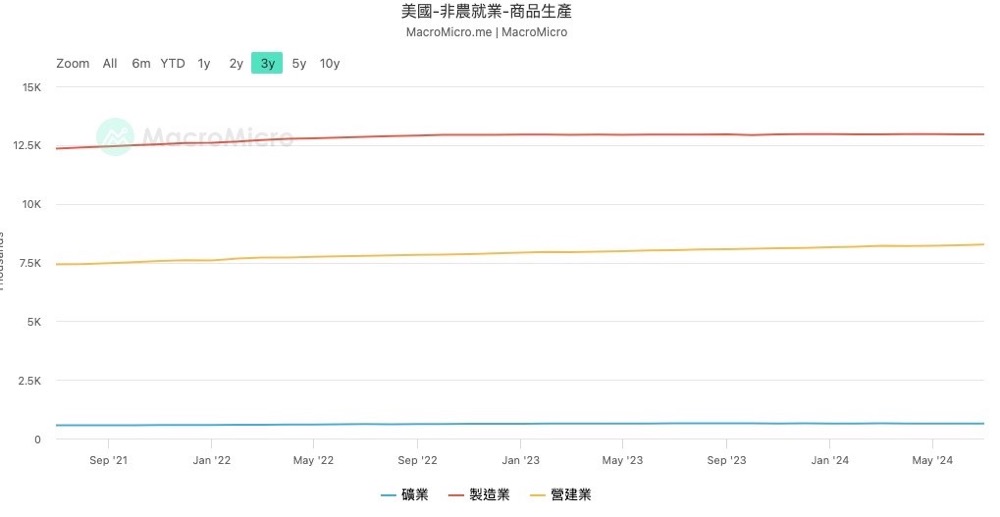
Let's take a closer look at the details of the non-farm payroll data to see what happened. We can see that in the commodity production category, there has been a long period of low volatility in the number of manufacturing jobs, with the construction industry contributing more to the data. For the US economy, high-end manufacturing, as well as the technology and financial services industries that match it, are the main driving forces. That is to say, when the income of this high-income elite increases, they are affected by the wealth effect and increase consumption, which in turn benefits other middle and low-end service industries. Therefore, the employment situation of this group of people can be used as a leading indicator of the overall employment situation in the US. The weakness of manufacturing employment may show certain fuse risks. In addition, let's take a look at the US ISM Manufacturing Index (PMI). We can see that the PMI is in a rapid downward trend, which further confirms the weak situation of the US manufacturing industry.
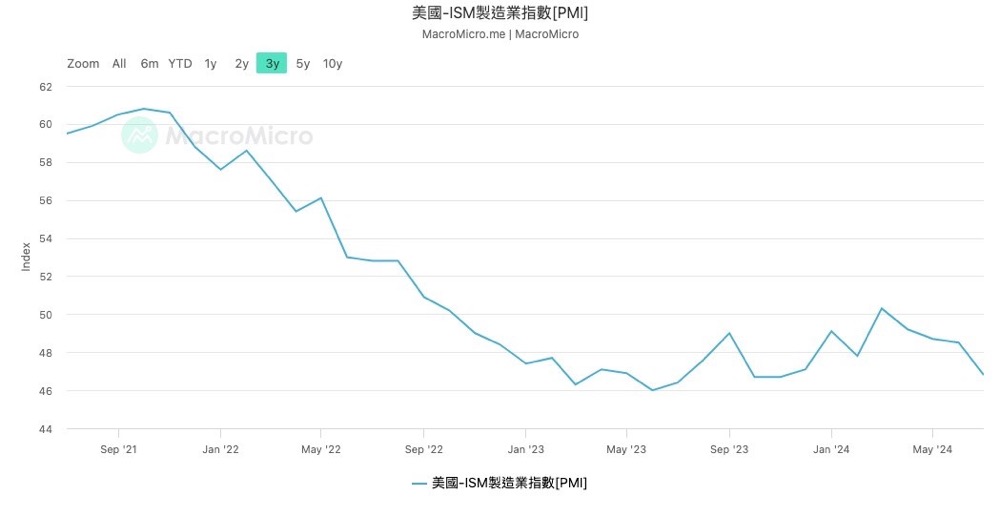
Next, let's take a look at the service industry. Both the professional technology industry and the retail industry have shown the same frozen situation. The main contributors to the indicators are education, healthcare, and leisure and entertainment. I think there are two main reasons. Firstly, there has been a certain fluctuation in COVID-19 recently, and due to the impact of hurricanes, there has been a certain shortage of related medical and rescue personnel. Secondly, due to the fact that most US people are on vacation in July, the tourism and other leisure and entertainment industries have grown. After the holiday ends, this field is bound to receive a certain blow.
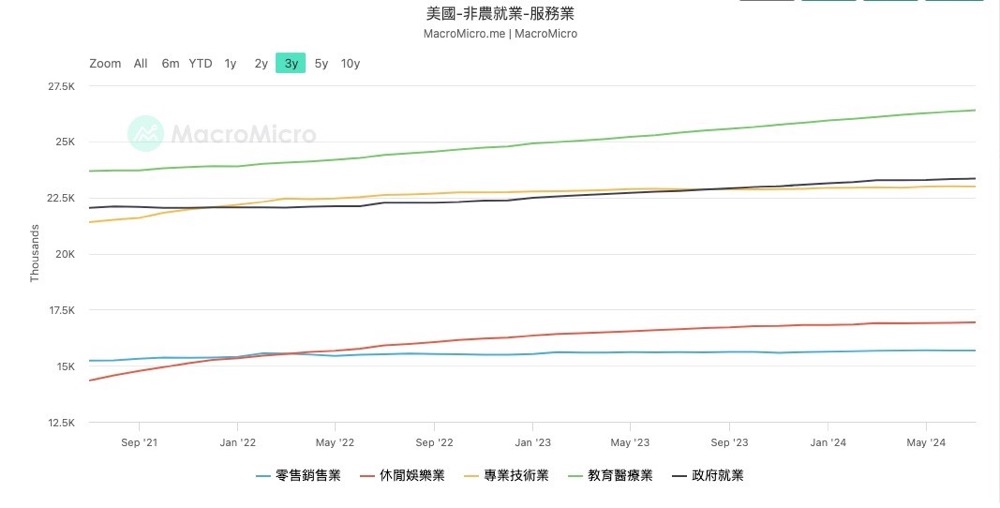
Therefore, overall, the current recession risk in the US still exists, so friends need to further observe related risks through macro data, mainly including non-farm employment, initial jobless claims, PMI, consumer confidence index CCI, housing price index, etc.
Risk 2: Rate cut rhythm
The second issue that needs attention is the pace of interest rate cuts. Although it has been confirmed that interest rate cuts have begun, the speed of interest rate cuts will affect the performance of the risk asset market. In history, emergency interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve are relatively rare, so economic fluctuations between interest rate meetings require the market's own interpretation to affect price trends. When some economic data indicates that the Federal Reserve is raising interest rates too slowly, the market will take the lead in reacting. Therefore, it is crucial to determine a suitable pace of interest rate cuts and guide the market to operate according to the Federal Reserve's goals through interest rate guidance.
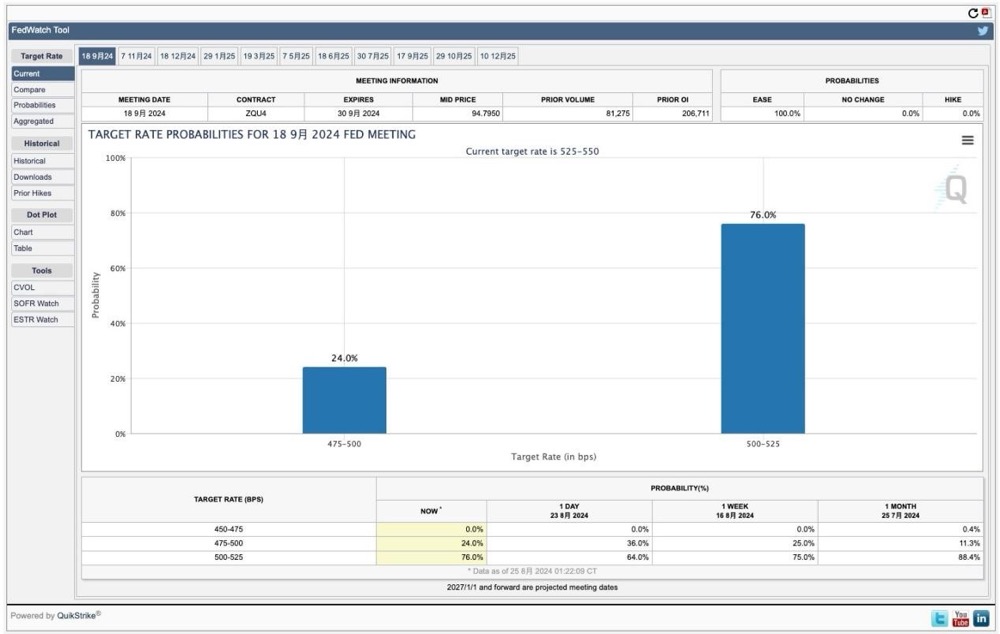
The current market estimate for the September interest rate decision is a nearly 75% probability of a 25-50 basis point drop, and a 25% probability of a 50-75 basis point drop. Therefore, closely monitoring the market's judgment can also clearly judge market sentiment.
Risk Three: QT Plan
Since the 2008 financial crisis, the Federal Reserve quickly lowered interest rates to 0, but still failed to revive the economy. At that time, Monetary Policy had already failed because it could not continue to cut interest rates. Therefore, in order to further inject liquidity into the market, the Federal Reserve created the Quantitative Easing QE tool, which injected liquidity into the market by expanding the Federal Reserve's Balance Sheet and increasing the reserve size of the banking system. This approach actually transfers market risks to the Federal Reserve. Therefore, in order to reduce systemic risks, the Federal Reserve needs to control the Balance Sheet size through quantitative tightening QT to avoid excessive risks caused by disorderly easing.
Powell's speech did not involve the judgment of the current QT plan and subsequent planning, so we still need to pay attention to the progress of QT and the changes in bank reserves caused by it.
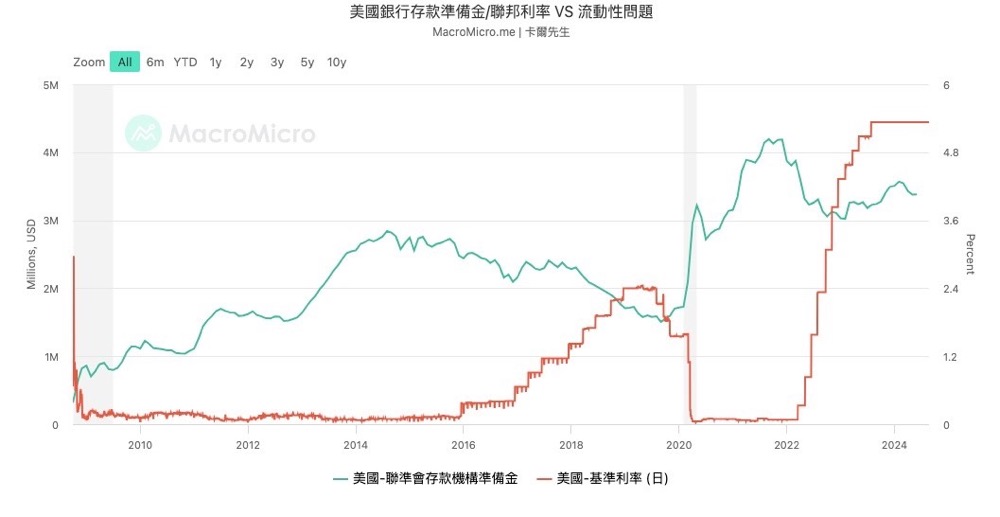
Risk 4: Inflation risk reignites
Powell maintained an optimistic attitude towards inflation risks at Friday's meeting. Although it did not reach the expected 2%, he is already confident in controlling inflation. Indeed, this judgment can be reflected in the data, and many economists have already begun to speculate whether the target inflation rate is still set at 2% after experiencing the baptism of the epidemic.
However, there are still some risks here.
Firstly, from a macro perspective, the re-industrialization of the US is not smooth due to various factors, and coincides with the US's anti-globalization policy under the background of Sino-US confrontation. The supply-side problem has not been fundamentally solved. Any geopolitical risks will exacerbate the reignition of inflation.
Secondly, considering that in this round of interest rate hike cycle, the US economy has not entered a substantial recession cycle. With the progress of interest rate cuts, the risk asset market will recover. When the wealth effect arises again, with the expansion of demand, service industry inflation will also reignite.
Finally, there is a problem with data statistics. We know that in order to avoid seasonal factors interfering with the data, CPI and PCE data usually use annual growth rates, that is, year-on-year data to reflect the real situation. Starting from May this year, the high base period factors of 2023 will be exhausted. At that time, the performance of relevant data will be easily affected by growth.
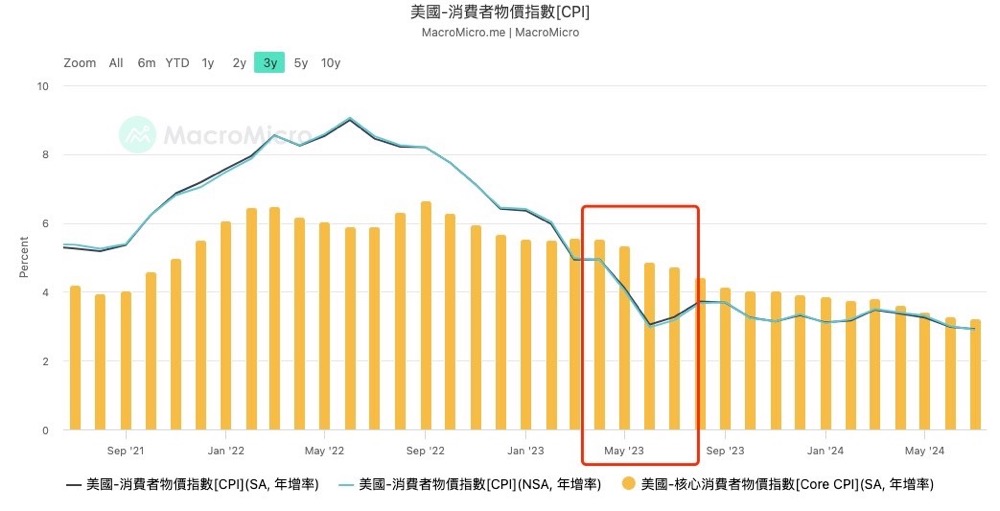

Risk 5: Efficiency of global central bank linkage
I think most of my friends still remember the risk of the Japan-US spread trade in early August. Although the Bank of Japan immediately intervened to calm the market, we can still see its hawkish attitude from the two days before the hearing of Ueda Kazuo. Moreover, during his speech, the yen also showed a significant rise and was restored after the officials' reassurance after the hearing. Of course, in fact, the macro data performance in Japan does indeed need to raise interest rates
This has also been analyzed in detail in my previous article However, as the core source of global leveraged funds for a long time, any interest rate hike dinner by the Bank of Japan will bring great uncertainty to the risk market. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain a high level of attention to its policies.
Risk 6: US Election Risk
Finally, I need to mention the risk of the US election. In my previous article, I have also analyzed in detail the economic policies of
Trump and
Harris . As the election approaches, there will be more and more confrontations and uncertainties, so it is also necessary to keep an eye on election-related matters.
2
0
Disclaimer: The content of this article solely reflects the author's opinion and does not represent the platform in any capacity. This article is not intended to serve as a reference for making investment decisions.
PoolX: Locked for new tokens.
APR up to 10%. Always on, always get airdrop.
Lock now!
You may also like
ARK Invest Raises 2030 Bitcoin Price Target to as High as $2.4M in Bullish Scenario
Cointime•2025/04/25 12:44

XRP News: What's on May 19 for XRP?
Cryptoticker•2025/04/25 12:11
ADA Explodes Past $0.70 — What Now?
Cryptoticker•2025/04/25 12:11
PEPE Dips Slightly – But Whales Are Still Accumulating. Should You Follow?
Pepe's funding rate has risen strongly in the past couple of days, one of several signals that more gains are coming.
CryptoNews•2025/04/25 09:55

Trending news
MoreCrypto prices
MoreBitcoin
BTC
$95,030.34
+1.68%
Ethereum
ETH
$1,801.63
+2.00%
Tether USDt
USDT
$1
+0.04%
XRP
XRP
$2.19
-0.44%
BNB
BNB
$603.61
+0.74%
Solana
SOL
$151.12
-0.36%
USDC
USDC
$0.9999
-0.01%
Dogecoin
DOGE
$0.1813
+0.16%
Cardano
ADA
$0.7166
-1.24%
TRON
TRX
$0.2433
-1.31%
How to sell PI
Bitget lists PI – Buy or sell PI quickly on Bitget!
Trade now
Become a trader now?A welcome pack worth 6200 USDT for new Bitgetters!
Sign up now