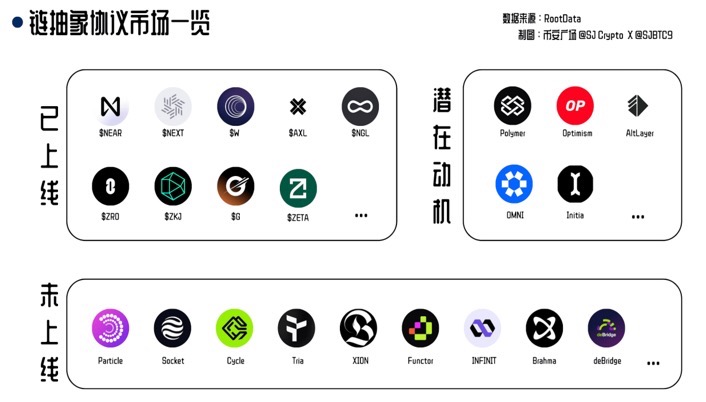
Ethereum Developers Introduce Hoodi Testnet for Upcoming Pectra Upgrade!!!
$ETH Ethereum developers have launched a new test network named Hoodi, which will facilitate the blockchain's forthcoming 'Pectra' upgrade. Scheduled to go live on Hoodi on March 26, the upgrade is expected to transition to Ethereum's mainnet approximately 30 days later, contingent on successful testing outcomes.
The creation of Hoodi follows unsuccessful Pectra tests on Ethereum’s other testnets, Holesky and Sepolia, which encountered configuration issues preventing proper finalization. These test networks, including Hoodi, are designed to replicate the main Ethereum network, providing developers a low-risk environment to trial code changes or significant upgrades like Pectra before mainnet deployment.
Initially, the Pectra upgrade was intended to activate on Ethereum after the tests on Holesky and Sepolia. However, due to complications, developers opted to establish Hoodi for another round of testing the ambitious Pectra upgrade. Hoodi is also anticipated to serve future testing needs.
Hoodi mirrors Ethereum’s mainnet by maintaining an equivalent number of validators on its network. Ethereum core developer Parithosh Jayanthi highlighted during a recent Ethereum core developers call that Hoodi would be instrumental for Ethereum staking pools and node operators to evaluate their infrastructure.
Holesky and Sepolia were constructed with distinct objectives: Holesky features a larger validator set than Ethereum’s mainnet, aimed at addressing scalability challenges, while Sepolia is a closed network exclusively for developers, intended for application testing.
The Pectra upgrade encompasses a series of enhancements designed to improve Ethereum's usability and efficiency for both developers and end-users. Notably, it introduces "smart contract" capabilities that could enable wallets to pay gas fees using cryptocurrencies other than ether (ETH)
_The Future of Sustainable Cities: A Comprehensive Guide to Green Buildings, Smart Infrastructure
The world is rapidly urbanizing, with cities expected to accommodate an additional 2.5 billion people by 2050. Sustainable cities are critical for mitigating climate change, improving public health, and enhancing quality of life. Green buildings, smart infrastructure, and renewable energy are essential components of sustainable cities, offering reduced environmental impact, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced economic benefits. In this article, we'll explore the future of sustainable cities, highlighting the benefits, challenges, and potential future developments of these technologies.
# Benefits of Green Buildings
Green buildings offer several benefits, including:
1. *Reduced Energy Consumption*: Green buildings can reduce energy consumption, using energy-efficient systems, renewable energy sources, and sustainable building materials.
2. *Improved Indoor Air Quality*: Green buildings can improve indoor air quality, using natural ventilation, air filtration systems, and non-toxic building materials.
3. *Enhanced Water Efficiency*: Green buildings can enhance water efficiency, using low-flow fixtures, greywater systems, and rainwater harvesting.
4. *Increased Property Value*: Green buildings can increase property value, providing a competitive advantage in the real estate market.
# Challenges of Green Buildings
Green buildings also face several challenges, including:
1. *Higher Upfront Costs*: Green buildings often require higher upfront costs, although these costs can be offset by long-term energy savings and increased property value.
2. *Limited Availability of Sustainable Materials*: Green buildings require sustainable materials, which can be limited in availability and higher in cost.
3. *Complexity of Green Building Certification*: Green building certification can be complex and time-consuming, requiring significant documentation and verification.
4. *Public Awareness and Education*: Green buildings require public awareness and education, addressing concerns about cost, complexity, and environmental impact.
# Benefits of Smart Infrastructure
Smart infrastructure offers several benefits, including:
1. *Improved Energy Efficiency*: Smart infrastructure can improve energy efficiency, using advanced sensors, smart grids, and energy management systems.
2. *Enhanced Public Safety*: Smart infrastructure can enhance public safety, using intelligent transportation systems, smart lighting, and emergency response systems.
3. *Increased Efficiency of Public Services*: Smart infrastructure can increase the efficiency of public services, using data analytics, smart water management, and waste management systems.
4. *Improved Quality of Life*: Smart infrastructure can improve quality of life, providing convenient, efficient, and sustainable services to citizens.
# Challenges of Smart Infrastructure
Smart infrastructure also faces several challenges, including:
1. *High Upfront Costs*: Smart infrastructure requires significant investment in hardware, software, and infrastructure, which can be a barrier for cities with limited budgets.
2. *Cybersecurity Risks*: Smart infrastructure faces cybersecurity risks, including data breaches, hacking, and system compromise.
3. *Interoperability and Standardization*: Smart infrastructure requires interoperability and standardization, ensuring seamless communication and data exchange between different systems and devices.
4. *Public Awareness and Education*: Smart infrastructure requires public awareness and education, addressing concerns about data privacy, security, and environmental impact.
# Benefits of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy offers several benefits, including:
1. *Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions*: Renewable energy can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating climate change and improving air quality.
2. *Improved Energy Security*: Renewable energy can improve energy security, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and promoting energy diversity.
3. *Enhanced Economic Benefits*: Renewable energy can provide enhanced economic benefits, creating jobs, stimulating local economies, and promoting sustainable development.
4. *Increased Energy Independence*: Renewable energy can increase energy independence, enabling cities and communities to generate their own energy and reduce reliance on external energy sources.
# Challenges of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy also faces several challenges, including:
1. *Intermittency*: Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are intermittent, requiring energy storage solutions to ensure a stable and reliable energy supply.
2. *High Upfront Costs*: Renewable energy requires significant investment in infrastructure, technology, and personnel, which can be a barrier for cities with limited budgets.
3. *Policy and Regulatory Frameworks*: Renewable energy requires supportive policy and regulatory frameworks, including tax incentives, net metering laws, and renewable portfolio standards.
4. *Public Acceptance and Education*: Renewable energy requires public acceptance and education, addressing concerns about cost, complexity, and environmental impact.
# Conclusion
Sustainable cities are critical for mitigating climate change, improving public health, and enhancing quality of life. Green buildings, smart infrastructure, and renewable energy are essential components of sustainable cities, offering reduced environmental impact, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced economic benefits. While these technologies face several challenges, including higher upfront costs, limited availability of sustainable materials, and cybersecurity risks, they offer significant benefits, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, improved energy security, and enhanced economic benefits. Understanding the benefits, challenges, and potential future developments of these technologies is critical for developing effective strategies to promote
# __The Future of Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide to EV Technology, Charging Infrastructure
The transportation sector is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by technological innovations, environmental concerns, and government policies. Electric vehicles (EVs) are at the forefront of this transformation, offering improved efficiency, reduced emissions, and enhanced sustainability. In this article, we'll explore the future of electric vehicles, highlighting the benefits, challenges, and potential future developments of EV technology, charging infrastructure, and sustainable transportation.
# Benefits of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles offer several benefits, including:
1. *Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions*: Electric vehicles can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating climate change and improving air quality.
2. *Improved Energy Efficiency*: Electric vehicles can achieve higher energy efficiency than traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, reducing energy consumption and costs.
3. *Lower Operating Costs*: Electric vehicles can provide lower operating costs, reducing fuel costs and maintenance expenses.
4. *Enhanced Performance*: Electric vehicles can offer enhanced performance, including faster acceleration and smoother operation.
# Challenges of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles also face several challenges, including:
1. *Limited Range and Charging Time*: Electric vehicles have limited range and charging time, requiring frequent recharging and potentially limiting long-distance travel.
2. *Higher Upfront Costs*: Electric vehicles often have higher upfront costs than traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, although costs are decreasing as technology improves.
3. *Charging Infrastructure*: Electric vehicles require a comprehensive charging infrastructure, including public charging stations and home charging systems.
4. *Battery Durability and Recycling*: Electric vehicles require durable and recyclable batteries, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact.
# Benefits of Charging Infrastructure
Charging infrastructure offers several benefits, including:
1. *Convenience and Accessibility*: Charging infrastructure can provide convenient and accessible charging options, reducing range anxiety and promoting EV adoption.
2. *Reduced Charging Time*: Charging infrastructure can reduce charging time, enabling faster and more efficient charging.
3. *Increased Efficiency*: Charging infrastructure can increase efficiency, optimizing energy transfer and reducing energy losses.
4. *Job Creation and Economic Growth*: Charging infrastructure can create jobs and stimulate economic growth, promoting sustainable transportation and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
# Challenges of Charging Infrastructure
Charging infrastructure also faces several challenges, including:
1. *High Upfront Costs*: Charging infrastructure requires significant investment in hardware, software, and installation, which can be a barrier for widespread adoption.
2. *Standardization and Interoperability*: Charging infrastructure requires standardization and interoperability, ensuring seamless communication and energy transfer between vehicles and charging systems.
3. *Public Acceptance and Education*: Charging infrastructure requires public acceptance and education, addressing concerns about safety, convenience, and environmental impact.
4. *Regulatory Frameworks*: Charging infrastructure requires regulatory frameworks that support the development and deployment of charging infrastructure, including incentives, tax credits, and permitting requirements.
# Benefits of Sustainable Transportation
Sustainable transportation offers several benefits, including:
1. *Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions*: Sustainable transportation can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating climate change and improving air quality.
2. *Improved Public Health*: Sustainable transportation can improve public health, reducing air pollution, promoting physical activity, and enhancing mental well-being.
3. *Enhanced Economic Benefits*: Sustainable transportation can provide enhanced economic benefits, creating jobs, stimulating local economies, and promoting sustainable development.
4. *Increased Energy Security*: Sustainable transportation can increase energy security, reducing dependence on fossil fuels, promoting energy diversity, and enhancing energy resilience.
# Challenges of Sustainable Transportation
Sustainable transportation also faces several challenges, including:
1. *High Upfront Costs*: Sustainable transportation requires significant investment in infrastructure, technology, and personnel, which can be a barrier for widespread adoption.
2. *Behavioral and Cultural Changes*: Sustainable transportation requires behavioral and cultural changes, promoting walking, cycling, and public transportation, and reducing reliance on personal vehicles.
3. *Policy and Regulatory Frameworks*: Sustainable transportation requires policy and regulatory frameworks that support sustainable transportation, including incentives, tax credits, and permitting requirements.
4. *Public Acceptance and Education*: Sustainable transportation requires public acceptance and education, addressing concerns about safety, convenience, and environmental impact.
# Conclusion
The future of electric vehicles, charging infrastructure, and sustainable transportation is being shaped by technological innovations, environmental concerns, and government policies. While these technologies face several challenges, including limited range, higher upfront costs, and regulatory frameworks, they offer significant benefits, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced economic benefits. Understanding the benefits, challenges, and potential future developments of these technologies is critical for developing effective strategies to promote sustainable transportation.
# Recommendations
1. *Invest in Electric Vehicle Technology*: Invest in electric vehicle technology, including battery development, charging infrastructure, and sustainable transportation systems.
2. *Develop Comprehensive Charging Infrastructure*: Develop comprehensive charging infrastructure, including public charging stations, home charging systems, and fast-charging corridors.
3. *Promote Sustainable Transportation*: Promote sustainable transportation, including walking, cycling, and
The Future of Renewable Energy: A Comprehensive Guide to Solar, Wind, Hydro, and Geothermal Power
Renewable energy is becoming increasingly important as the world transitions away from fossil fuels and towards a more sustainable and environmentally-friendly energy mix. Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal power are four of the most promising renewable energy sources, offering reduced greenhouse gas emissions, improved energy security, and enhanced economic benefits. In this article, we'll explore the future of renewable energy, highlighting the benefits, challenges, and potential future developments of these technologies.
# Benefits of Solar Power
Solar power offers several benefits, including:
1. *Renewable and Sustainable*: Solar power is a renewable and sustainable energy source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
2. *Zero Emissions*: Solar power generates electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other pollutants, improving air quality and public health.
3. *Energy Independence*: Solar power can provide energy independence, enabling individuals and communities to generate their own electricity and reduce reliance on grid power.
4. *Economic Benefits*: Solar power can create jobs, stimulate local economies, and provide cost savings for individuals and businesses.
# Challenges of Solar Power
Solar power also faces several challenges, including:
1. *Intermittency*: Solar power is an intermittent energy source, requiring energy storage solutions to ensure a stable and reliable energy supply.
2. *High Upfront Costs*: Solar power requires significant investment in infrastructure, including solar panels, inverters, and mounting systems.
3. *Land Requirements*: Solar power requires large areas of land, potentially competing with agricultural or conservation uses.
4. *Policy and Regulatory Frameworks*: Solar power requires supportive policy and regulatory frameworks, including tax incentives, net metering laws, and renewable portfolio standards.
# Benefits of Wind Power
Wind power offers several benefits, including:
1. *Renewable and Sustainable*: Wind power is a renewable and sustainable energy source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
2. *Low Operating Costs*: Wind power has low operating costs, requiring minimal maintenance and repair.
3. *Scalability*: Wind power can be deployed at various scales, from small residential installations to large commercial wind farms.
4. *Economic Benefits*: Wind power can create jobs, stimulate local economies, and provide cost savings for individuals and businesses.
# Challenges of Wind Power
Wind power also faces several challenges, including:
1. *Intermittency*: Wind power is an intermittent energy source, requiring energy storage solutions to ensure a stable and reliable energy supply.
2. *Noise and Visual Pollution*: Wind power can generate noise and visual pollution, potentially impacting local communities and wildlife.
3. *Wildlife Concerns*: Wind power can pose risks to wildlife, particularly birds and bats, requiring careful siting and mitigation measures.
4. *Policy and Regulatory Frameworks*: Wind power requires supportive policy and regulatory frameworks, including tax incentives, net metering laws, and renewable portfolio standards.
# Benefits of Hydro Power
Hydro power offers several benefits, including:
1. *Renewable and Sustainable*: Hydro power is a renewable and sustainable energy source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
2. *High Energy Conversion Efficiency*: Hydro power has high energy conversion efficiency, generating electricity from the energy of moving water.
3. *Low Operating Costs*: Hydro power has low operating costs, requiring minimal maintenance and repair.
4. *Flood Control and Water Management*: Hydro power can provide flood control and water management benefits, regulating water flows and preventing damage to surrounding communities.
# Challenges of Hydro Power
Hydro power also faces several challenges, including:
1. *Dependence on Water Resources*: Hydro power is dependent on water resources, requiring significant rainfall or snowmelt to generate electricity.
2. *Environmental Concerns*: Hydro power can pose environmental concerns, particularly related to fish migration, habitat disruption, and water quality impacts.
3. *High Upfront Costs*: Hydro power requires significant investment in infrastructure, including dams, turbines, and transmission systems.
4. *Policy and Regulatory Frameworks*: Hydro power requires supportive policy and regulatory frameworks, including licensing, permitting, and environmental regulations.
# Benefits of Geothermal Power
Geothermal power offers several benefits, including:
1. *Renewable and Sustainable*: Geothermal power is a renewable and sustainable energy source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change.
2. *Baseload Power*: Geothermal power can provide baseload power, generating electricity continuously and reliably.
3. *Low Operating Costs*: Geothermal power has low operating costs, requiring minimal maintenance and repair.
4. *Scalability*: Geothermal power can be deployed at various scales, from small residential installations to large commercial power plants.
# Challenges of Geothermal Power
Geothermal power also faces several challenges, including:
1. *Limited Geographic Suitability*: Geothermal power is limited to areas with suitable geology, requiring significant exploration and development efforts.
2. *High Upfront Costs*: Geothermal power


 Precio más bajo
Precio más bajo Precio más alto
Precio más alto