Bitget beginner's guide: How to set TP and SL orders
In crypto futures trading, take-profit orders and stop-loss orders are essential risk management tools. They help traders lock in profits or limit potential losses during times of high market volatility. This article walks you through how to set TP/SL orders on Bitget, complete with practical examples and important tips.
|
Long/short |
Trigger price |
TP/SL |
|
Buy long |
Trigger price ≥ last price (futures price or mark price) |
SL |
|
Trigger price < last price (futures price or mark price) |
TP |
|
|
Sell short |
Trigger price ≤ last price (futures price or mark price) |
SL |
|
Trigger price > last price (futures price or mark price) |
TP |
1. What are TP and SL orders
Take-profit order
A take-profit (TP) order is a preset command that triggers the system to automatically execute sell or close orders to lock in unrealized profits when the price of a traded cryptocurrency reaches the TP price level.
• Basic TP: Triggers at a fixed price. For example, if you buy an asset at $80 and set TP at $100, the system will sell automatically when the price hits $100.
• Trailing stop: Dynamically adjusts the TP price in response to market movements. For instance, if you set a 5% trailing TP, the trigger price moves upward with the market and executes a sell order if the price drops by 5%.
Example: You buy BTCUSDT at $50,000 and set a take-profit at $55,000. Once the price reaches $55,000, Bitget will automatically close the position and lock in a $5000 profit.
Stop-loss order
A stop-loss (SL) order is a preset command that triggers the system to automatically execute sell or close orders to prevent potential losses when the price of a traded cryptocurrency reaches the SL price level.
• Basic stop-loss order: Triggers at a fixed price. For example, if you buy at $100 and set SL at $95, the position will be closed if the price falls to $95.
• MMR-based stop-loss: Triggers when your maintenance margin ratio drops below the set threshold. The system will automatically close your position to prevent further losses — particularly useful for high-leverage trades.
Example: You go long on BTCUSDT at $60,000 and set a stop-loss at $58,000. If the price drops to $58,000, your position will be closed to avoid further loss.
Bitget supports TP/SL functionality for both long and short positions. Once the last traded price reaches your preset trigger price, the system will close the position at the best available price.
2. How to set a TP order
1. Go to the trading page: Open the Bitget app and navigate to the Futures trading page. If you haven't opened a position, you can set TP on the order placement page. If you already have an open position, go to the Positions tab.
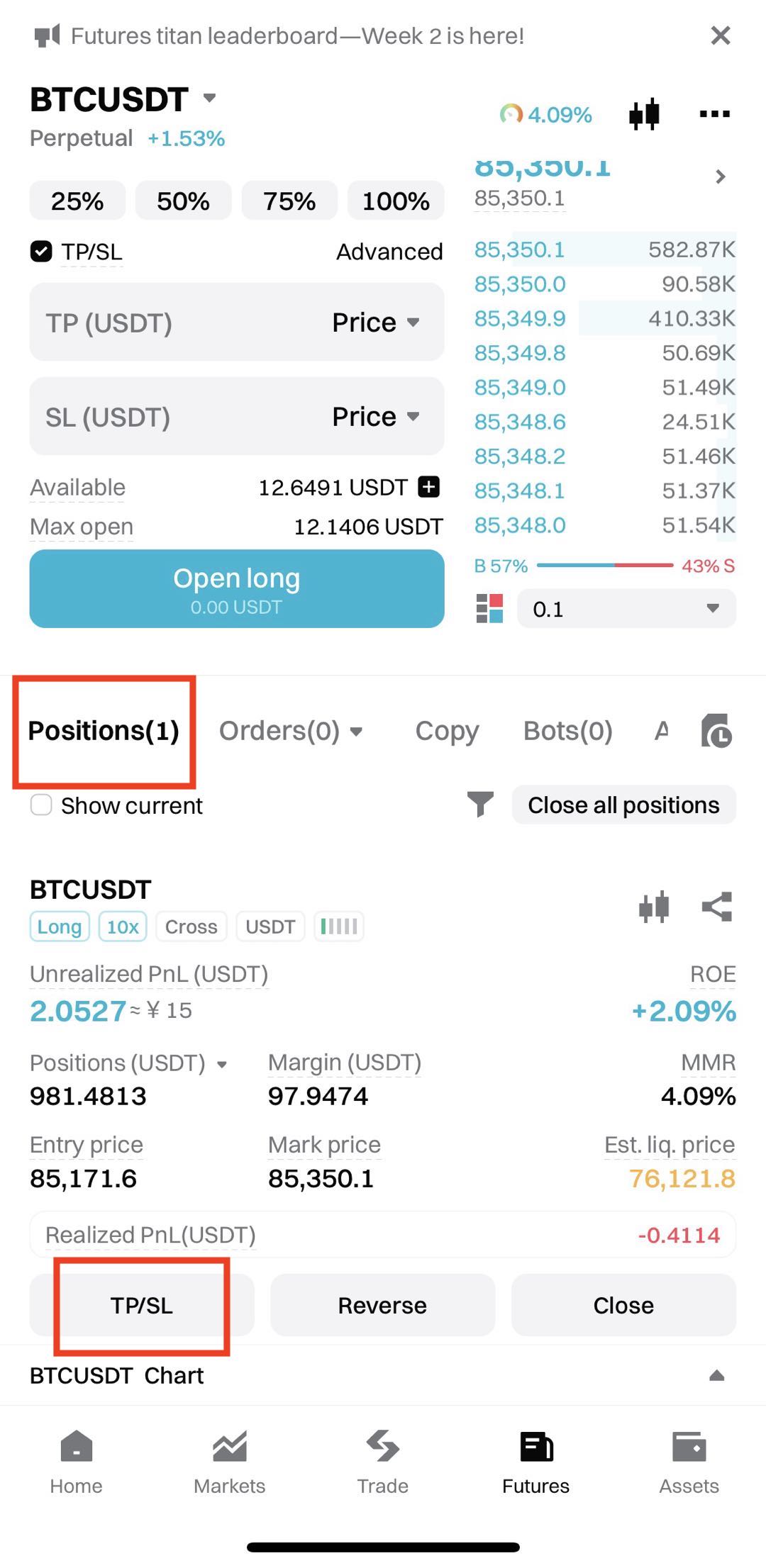
2. Find the TP settings: In the Positions tab, tap TP/SL next to your active position.
3. Enter your TP price: Enter a target price based on your trading strategy or technical indicators (e.g., support level or resistance level). For example, if you bought BTC at $71,000, you might set the TP at $75,000.
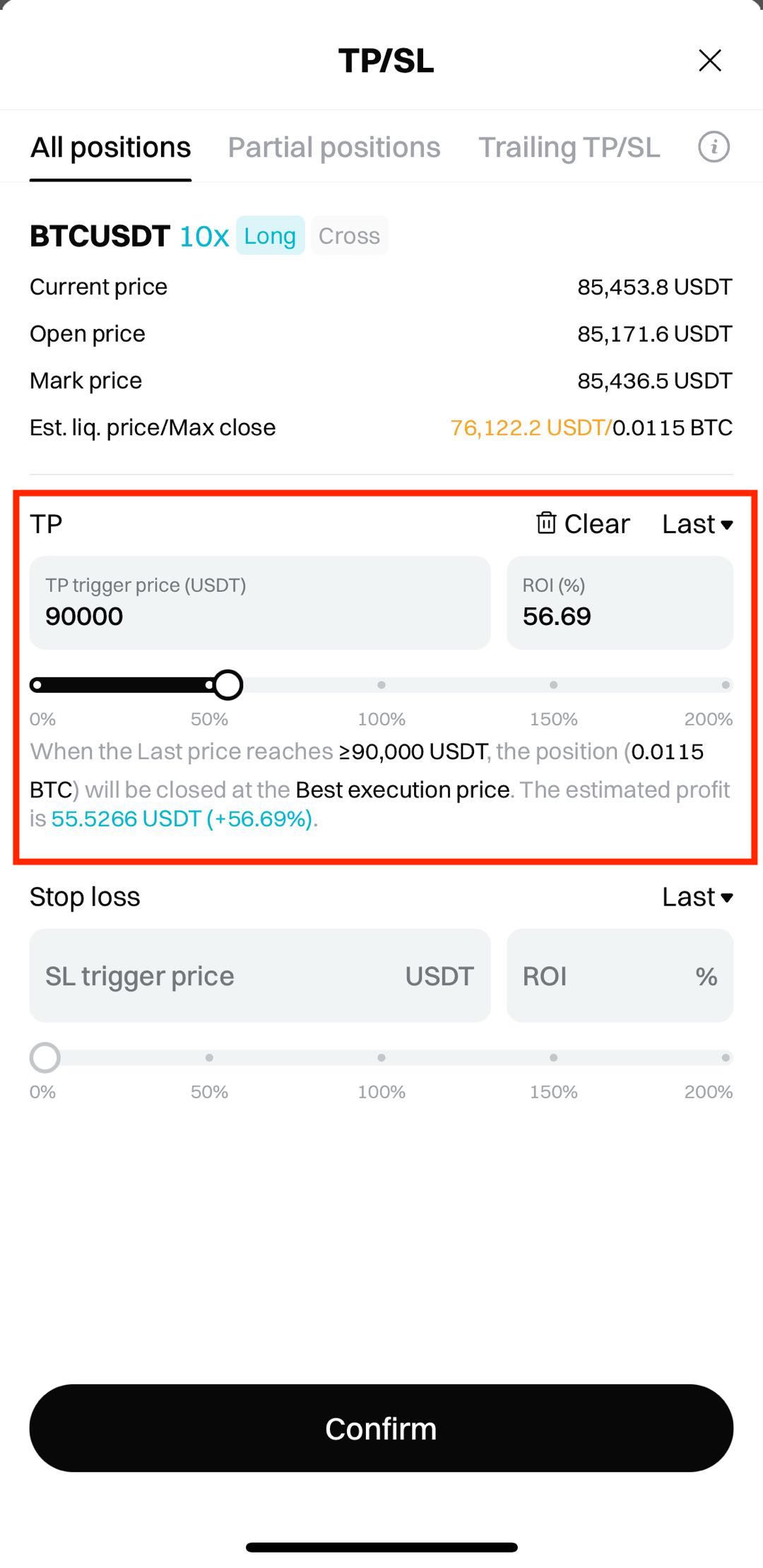
4. Confirm your settings: Double-check the TP price and order quantity, then tap Confirm.
5. Edit or cancel: If needed, go to the Positions tab and find your TP order. Tap Edit to update your TP or Cancel to remove it.
Example
• Futures order: BTCUSDT
• Current price: $80,000
• TP price: $82,000
• You can later adjust it to $83,000 or cancel the TP order as market conditions change.
3. How to set a SL order
1. Go to the trading page: Open the Bitget app and navigate to the Futures trading page. If you haven't opened a position yet, you can set SL on the order placement page. If you already have an open position, go to the Positions tab.
2. Find the SL settings: In the Positions tab, tap TP/SL next to your active position.
3. Enter your SL price: Enter a target price based on your risk tolerance or technical indicators. For example, if you bought BTC at $71,000, you might set the SL at $68,000.
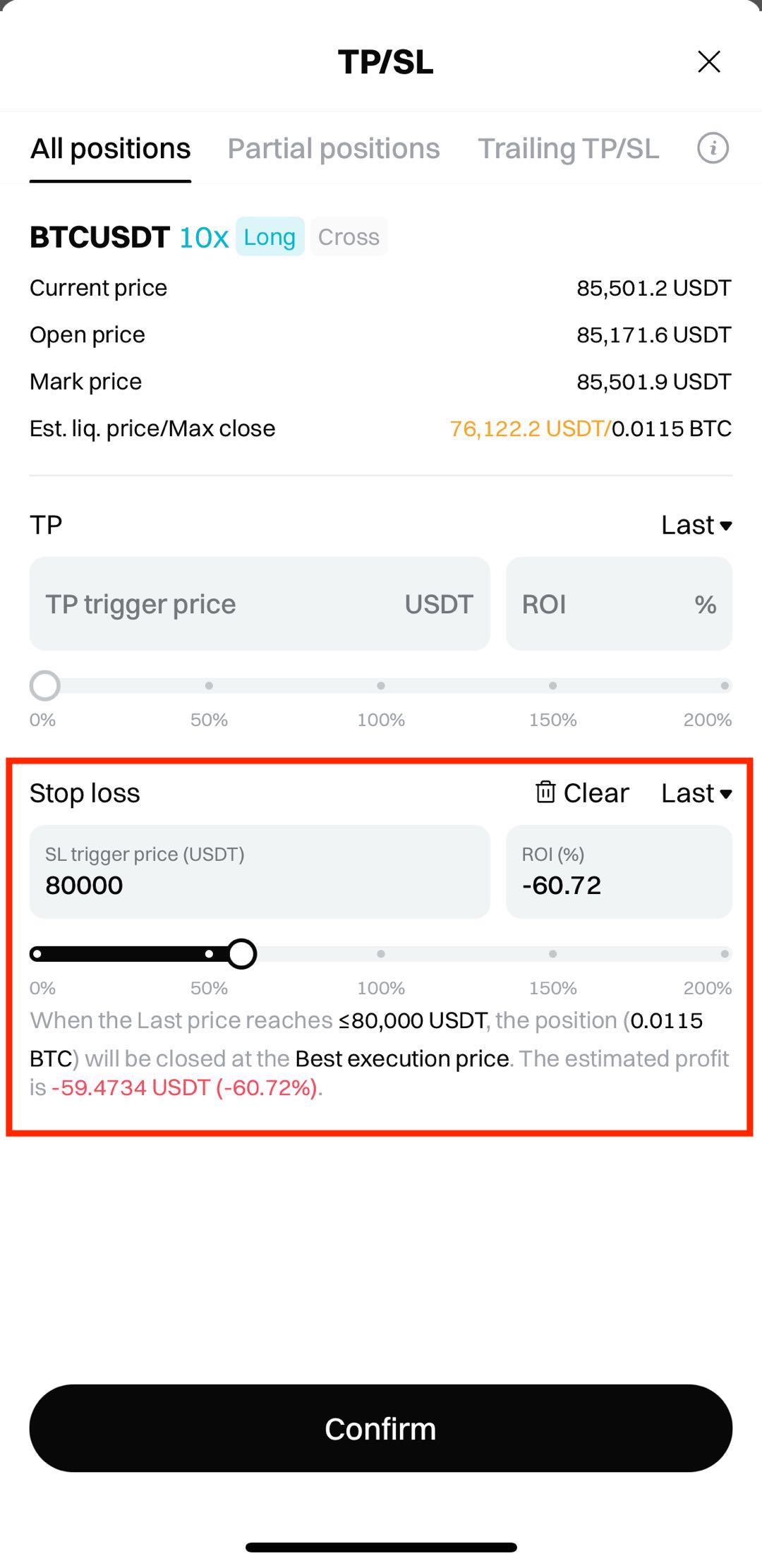
4. Confirm your settings: Double check the SL price and order quantity, then tap Confirm.
5. Edit or cancel: If needed, go to the Positions tab, find your SL order. Tap Modify to update your SL or Cancel to remove it.
Example
• Futures order: BTCUSDT
• Current price: $80,000
• SL price: $78,000
• You can later adjust it to $77,000 or cancel the SL order as market conditions change.
4. Important tips
• Adjust dynamically: Update your TP/SL levels based on market trends. If the trend is favorable, raise your TP. If unfavorable, tighten your SL.
• Match your trading strategies: Conservative traders can use narrower TP/SL ranges. For volatile markets, consider setting a wider range.
• Beware of market risks: In fast-moving markets, TP/SL orders may not be fully executed due to slippage. Make sure you understand how the TP/SL feature works before using it.
• Stay alert: While TP/SL orders help automate risk management, it's still important to actively monitor market movements and adjust your strategy as needed.
By using take-profit and stop-loss orders effectively, Bitgetters can better manage risk and maximize returns in the crypto market. Be sure to combine these tools with real-time market analysis and your personal trading goals.
Related articles
Share

