Bitget futures: A complete guide to scaled orders
1. What are scaled orders?
A scaled order is an advanced order type offered by Bitget that allows users to split a large order into multiple smaller ones, which are placed automatically across a preset price range. You can customize the minimum and maximum prices, total quantity, order quantity, and size distribution (flat, ascending, or descending) to align with your trading strategy with high flexibility.
The key advantage of scaled orders is that they reduce the impact of large trades on the market while improving execution rates across various price levels—especially useful in volatile crypto markets.
2. When to use scaled orders
Scaled orders are useful in a variety of trading scenarios, particularly when you need greater precision in position management or cost control. Common use cases include:
• Minimizing market impact: Large orders in low-liquidity markets may trigger sharp price movements. Scaled orders break up the order into smaller chunks to reduce slippage.
• Targeting a price range: When you expect the price to fluctuate within a specific range, scaled orders allow you to place orders at multiple price levels within that range, increasing the chances of execution.
• Cost optimization: Scaled orders allow users to build a position at an average price, reducing the risk of entering a trade at a single unfavorable price point.
• Automated execution: Ideal for traders who want to place multiple orders without actively monitoring the market.
3. How it works (with example)
The core principle of scaled orders is to break a large order into smaller portions and place them across a specified price range based on your selected size distribution method. Each order is executed as the market price reaches its assigned level. Here is an example of how this works:
Case: Opening a BTC position with a scaled order
Suppose you want to open a long position in BTCUSDT perpetual futures with an investment of 10,000 USDT and a target price range of 50,000–52,000 USDT. You set the following parameters:
• Lowest price: 50,000 USDT
• Highest price: 52,000 USDT
• Order quantity: 5
• Total quantity: 0.2 BTC
• Size distribution: Flat (equal size in each order)
Execution:
1. The system divides the 50,000–52,000 USDT range into 5 price levels: 50,000 USDT, 50,500 USDT, 51,000 USDT, 51,500 USDT, and 52,000 USDT.
2. In the flat mode, 0.2 BTC is split evenly into 5 orders, with 0.04 BTC per order.
3. Orders are placed at each level and filled as the market price reaches those levels.
4. If the price soars quickly, some higher-level orders may remain unfilled. You can adjust your strategy accordingly.
Outcome: You built a position at an average price of around 51,000 USDT, which helps you save on entry costs compared to placing the full 0.2 BTC at 52,000 USDT in a single order.
4. How to place a scaled order (step-by-step)
Bitget supports scaled orders on both the web and mobile app. Here's how to get started:
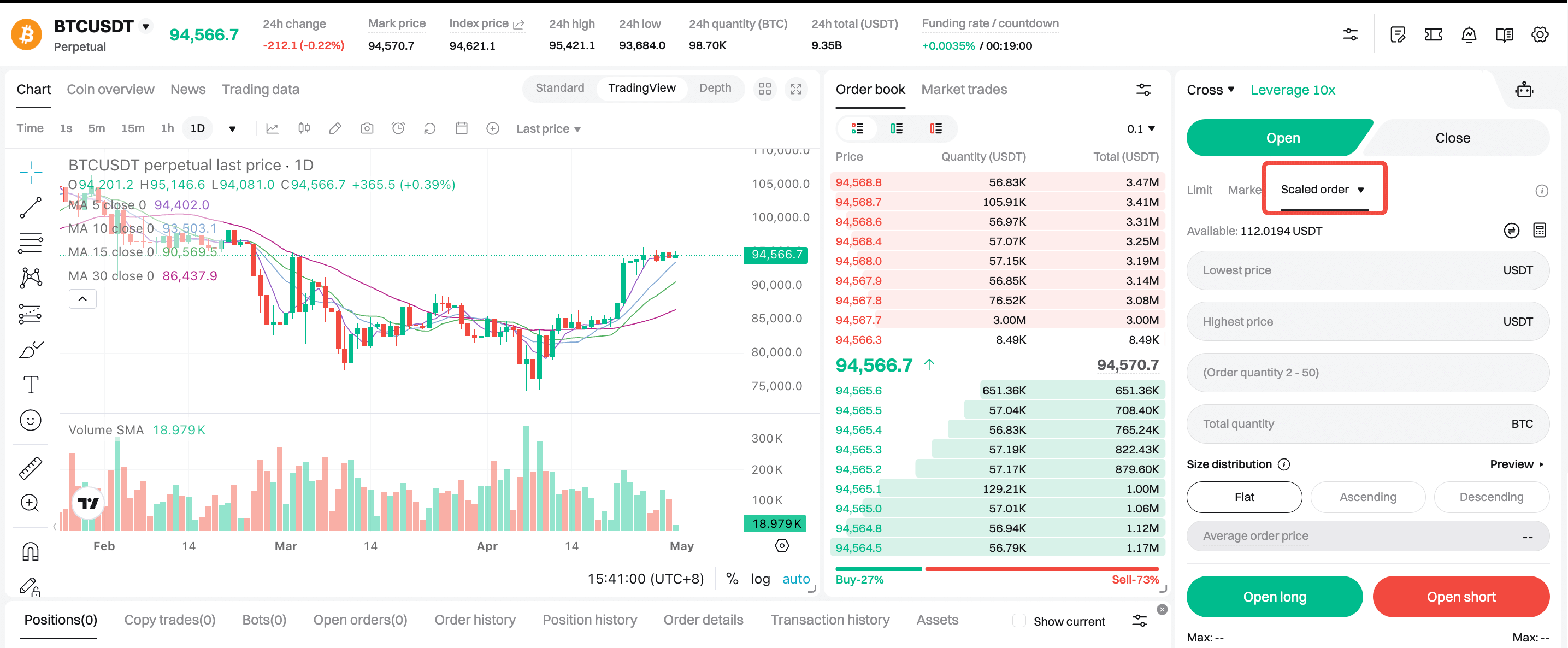
4.1 On the website
1. Log in: Visit the Bitget website and log in to your account.
2. Go to the futures trading page: Click Futures in the top navigation bar and head to the futures trading page. Select your desired trading pair (e.g., BTCUSDT perpetual futures).
3. Select scaled order: In the order panel on the right, open the Order Type dropdown and select Scaled Order.
4. Set order parameters:
○ Direction: Choose Long or Short, and set your leverage (e.g., 20x).
○ Set the lowest and highest prices for the price range.
○ Enter the order quantity (2–50 orders) and the total quantity (e.g. 0.2 BTC).
○ Size distribution method: Choose Flat, Ascending, or Descending.
5. Preview your order: Click Preview to see how the orders will be distributed by price and quantity. Double-check the details before proceeding.
6. Place the order: Ensure you have sufficient balance, then click Open Long or Open Short to submit. The system will automatically place the orders in the market.
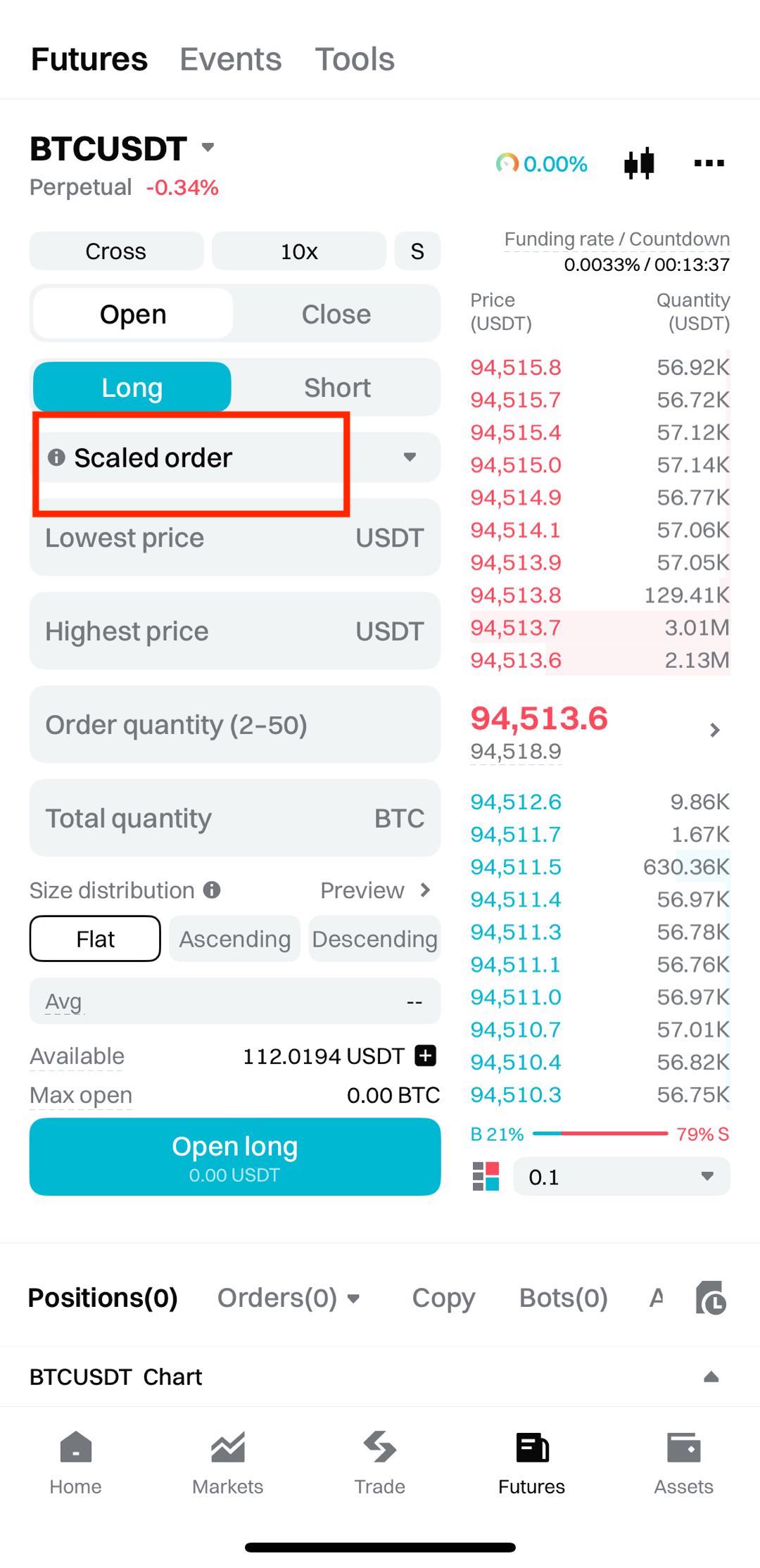
4.2 On the app:
1. Open the app: Download and log in to the Bitget app.
2. Access futures trading: Tap Futures on the home screen and select your target trading pair (e.g., BTCUSDT).
3. Select scaled order: In the order section, switch to Scaled Order mode.
4. Set your parameters: As with the website, set your direction, leverage, price range, order quantity, total quantity, and size distribution method.
5. Confirm the order: Preview the order details. Once confirmed, tap Open Long or Open Short to submit.
Tip: Before submitting, always review the order confirmation screen. The system will alert you if any part of the order may execute immediately, helping you avoid unintended or premature execution.
Related articles
• Bitget beginner's guide — Introduction to futures order types
Share

